2024
XTSFormer: Cross-Temporal-Scale Transformer for Irregular-Time Event Prediction in Clinical Applications
Tingsong Xiao, Zelin Xu, Wenchong He, Zhengkun Xiao, Yupu Zhang, Zibo Liu, Shigang Chen, My T. Thai, Jiang Bian, Parisa Rashidi, Zhe Jiang
The 39th Annual AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence (AAAI 2025)
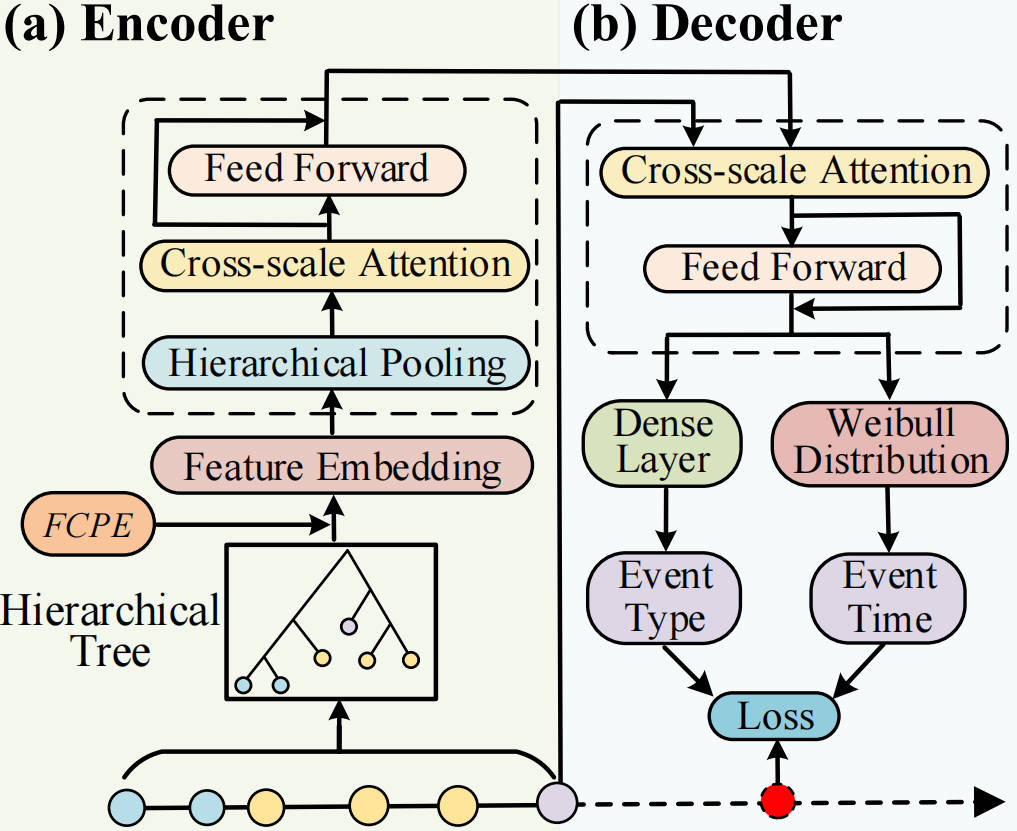
Modeling irregularly timed clinical events from EHRs is challenging due to time irregularity, cyclical patterns, and multi-scale event interactions. We propose XTSFormer, a transformer-based model with cycle-aware time encoding and multi-scale attention to address these challenges.
XTSFormer: Cross-Temporal-Scale Transformer for Irregular-Time Event Prediction in Clinical Applications
Tingsong Xiao, Zelin Xu, Wenchong He, Zhengkun Xiao, Yupu Zhang, Zibo Liu, Shigang Chen, My T. Thai, Jiang Bian, Parisa Rashidi, Zhe Jiang
The 39th Annual AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence (AAAI 2025)
Modeling irregularly timed clinical events from EHRs is challenging due to time irregularity, cyclical patterns, and multi-scale event interactions. We propose XTSFormer, a transformer-based model with cycle-aware time encoding and multi-scale attention to address these challenges.
Spatial-Logic-Aware Weakly Supervised Learning for Flood Mapping on Earth Imagery
Zelin Xu, Tingsong Xiao, Wenchong He, Yu Wang, Zhe Jiang, Shigang Chen, Yiqun Xie, Xiaowei Jia, Da Yan, Yang Zhou
The 38th Annual AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence (AAAI 2024)
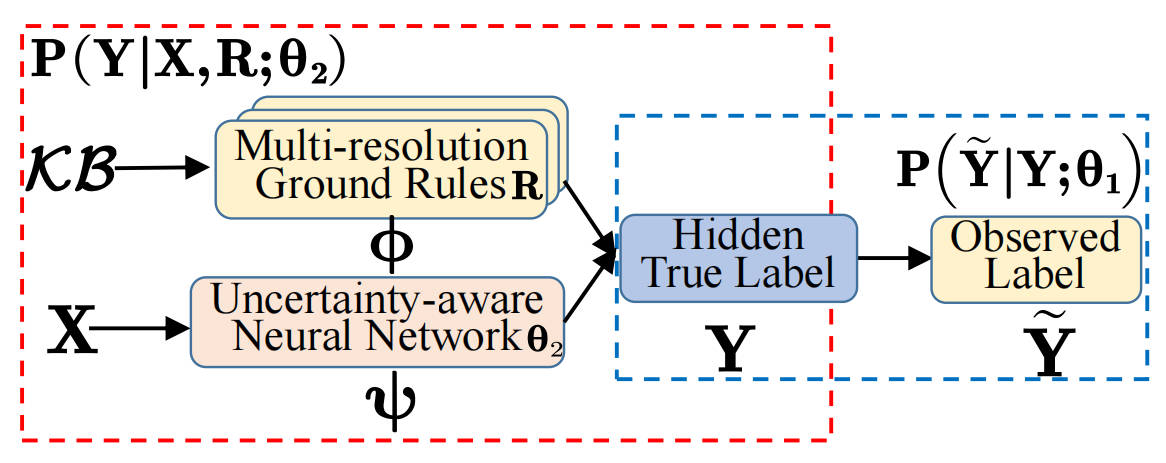
This work addresses the challenge of flood mapping on high-resolution Earth imagery with coarse, noisy labels by proposing a spatial-logic-aware weakly supervised learning framework. The framework integrates symbolic spatial logic inference with probabilistic learning and introduces a multi-resolution spatial reasoning algorithm to handle high-resolution imagery efficiently. Experiments on real-world flood datasets demonstrate superior prediction accuracy compared to traditional and neural-symbolic baselines.
Spatial-Logic-Aware Weakly Supervised Learning for Flood Mapping on Earth Imagery
Zelin Xu, Tingsong Xiao, Wenchong He, Yu Wang, Zhe Jiang, Shigang Chen, Yiqun Xie, Xiaowei Jia, Da Yan, Yang Zhou
The 38th Annual AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence (AAAI 2024)
This work addresses the challenge of flood mapping on high-resolution Earth imagery with coarse, noisy labels by proposing a spatial-logic-aware weakly supervised learning framework. The framework integrates symbolic spatial logic inference with probabilistic learning and introduces a multi-resolution spatial reasoning algorithm to handle high-resolution imagery efficiently. Experiments on real-world flood datasets demonstrate superior prediction accuracy compared to traditional and neural-symbolic baselines.
2023
A Hierarchical Spatial Transformer for Massive Point Samples in Continuous Space
Wenchong He, Zhe Jiang, Tingsong Xiao, Zelin Xu, Shigang Chen, Ronald Fick, Miles Medina, Christine Angelini
The 37th Annual Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems (NeurIPS 2023)
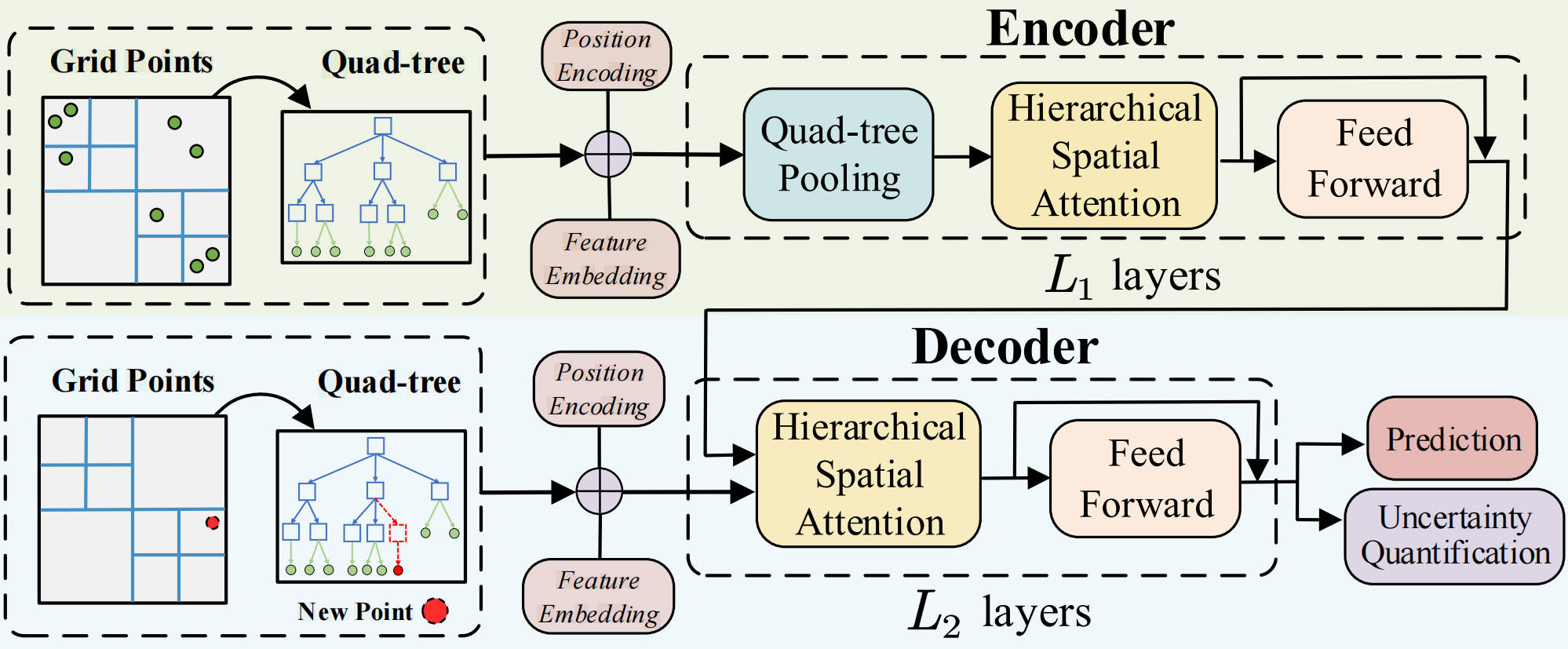
This paper proposes a hierarchical spatial transformer for massive point samples, addressing challenges like long-range dependencies, irregular distributions, and high computational costs. Using quad-tree-based multi-resolution learning, efficient spatial attention, and uncertainty quantification, the model outperforms baselines and scales to one million points on a single NVIDIA A100 GPU.
A Hierarchical Spatial Transformer for Massive Point Samples in Continuous Space
Wenchong He, Zhe Jiang, Tingsong Xiao, Zelin Xu, Shigang Chen, Ronald Fick, Miles Medina, Christine Angelini
The 37th Annual Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems (NeurIPS 2023)
This paper proposes a hierarchical spatial transformer for massive point samples, addressing challenges like long-range dependencies, irregular distributions, and high computational costs. Using quad-tree-based multi-resolution learning, efficient spatial attention, and uncertainty quantification, the model outperforms baselines and scales to one million points on a single NVIDIA A100 GPU.
M-GCN: Multi-scale Graph Convolutional Network for 3D Point Cloud Classification
Jing Hu, Xincheng Wang, Ziheng Liao, Tingsong Xiao# (# corresponding author)
IEEE International Conference on Multimedia and Expo (ICME 2023)
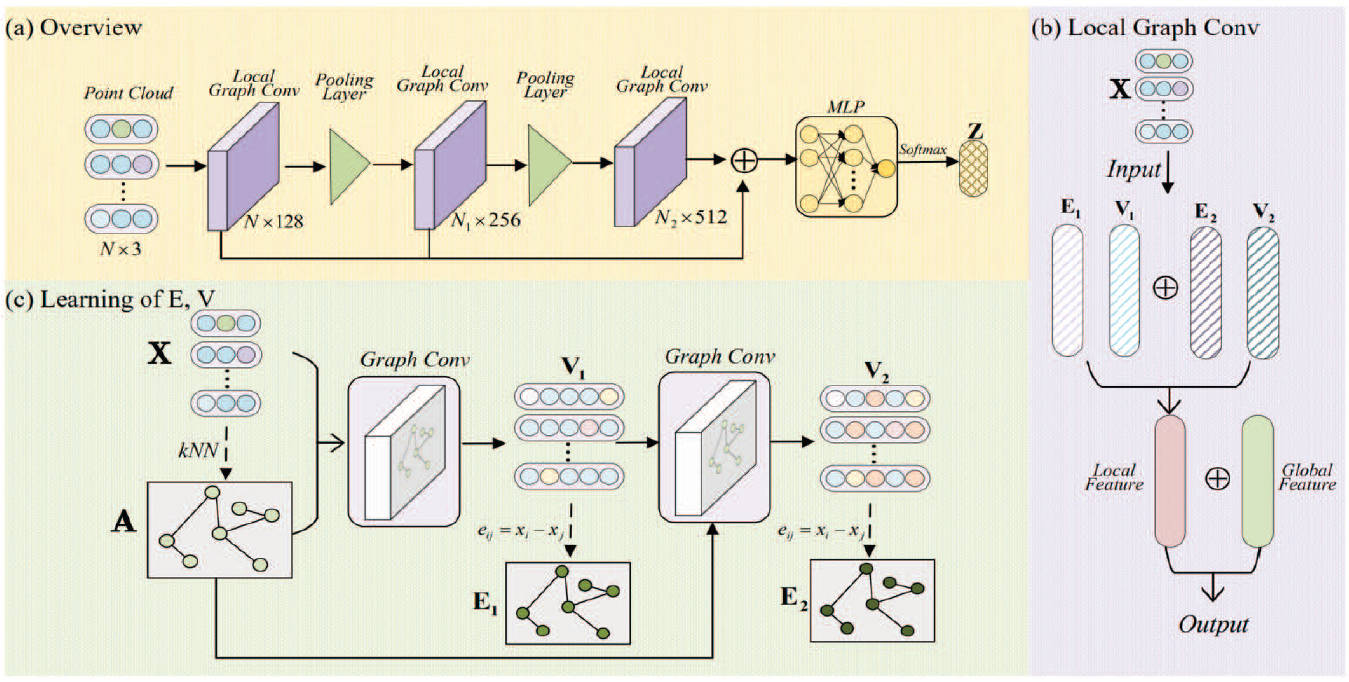
This paper introduces a Multi-Scale Graph Convolutional Network (M-GCN) to enhance 3D point cloud analysis by leveraging multi-scale feature fusion for richer local topological representations. By extracting geometric features across scales, M-GCN improves the representation power of point clouds. Experiments on ModelNet40 demonstrate state-of-the-art performance in 3D point cloud classification.
M-GCN: Multi-scale Graph Convolutional Network for 3D Point Cloud Classification
Jing Hu, Xincheng Wang, Ziheng Liao, Tingsong Xiao# (# corresponding author)
IEEE International Conference on Multimedia and Expo (ICME 2023)
This paper introduces a Multi-Scale Graph Convolutional Network (M-GCN) to enhance 3D point cloud analysis by leveraging multi-scale feature fusion for richer local topological representations. By extracting geometric features across scales, M-GCN improves the representation power of point clouds. Experiments on ModelNet40 demonstrate state-of-the-art performance in 3D point cloud classification.
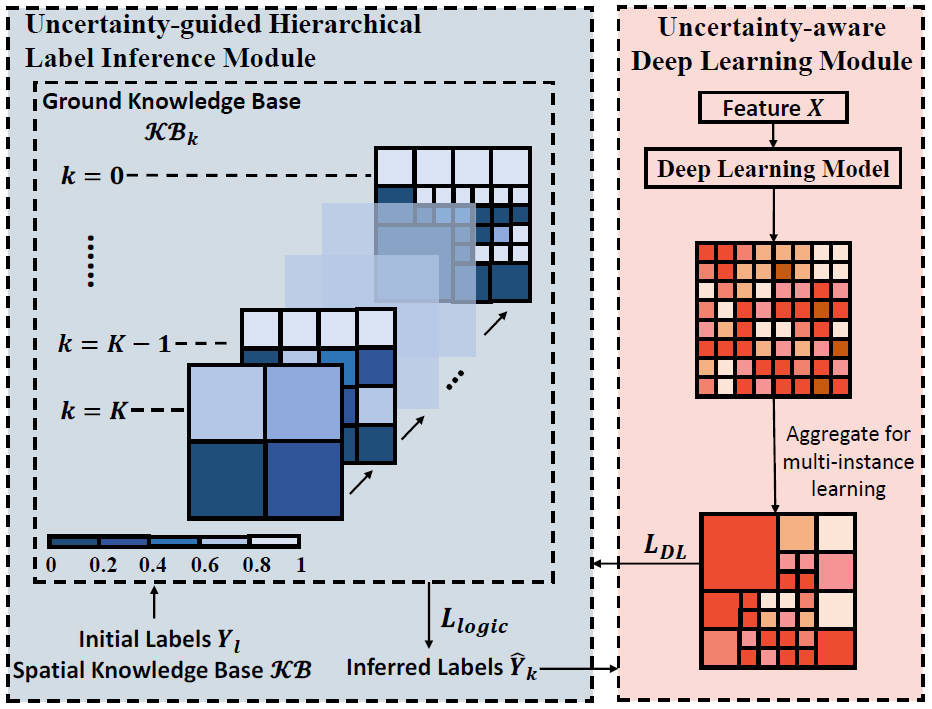
Spatial Knowledge-Infused Hierarchical Learning: An Application in Flood Mapping on Earth Imagery
Zelin Xu, Tingsong Xiao, Wenchong He, Yu Wang, Zhe Jiang
The 31st ACM International Conference on Advances in Geographic Information Systems (SIGSPATIAL 2023) Best Paper Award
This paper proposes a Spatial Knowledge-Infused Hierarchical Learning (SKI-HL) framework for Earth imagery with limited training labels, addressing challenges like sparse input labels, spatial uncertainty, and high computational costs. SKI-HL iteratively infers labels within a multi-resolution hierarchy using uncertainty-aware modules for selective label inference and neural network training. Experiments on flood mapping datasets demonstrate superior performance compared to baseline methods.
Spatial Knowledge-Infused Hierarchical Learning: An Application in Flood Mapping on Earth Imagery
Zelin Xu, Tingsong Xiao, Wenchong He, Yu Wang, Zhe Jiang
The 31st ACM International Conference on Advances in Geographic Information Systems (SIGSPATIAL 2023) Best Paper Award
This paper proposes a Spatial Knowledge-Infused Hierarchical Learning (SKI-HL) framework for Earth imagery with limited training labels, addressing challenges like sparse input labels, spatial uncertainty, and high computational costs. SKI-HL iteratively infers labels within a multi-resolution hierarchy using uncertainty-aware modules for selective label inference and neural network training. Experiments on flood mapping datasets demonstrate superior performance compared to baseline methods.
Pharetra Massa Massa Ultricies Mi Nisl Tincidunt
Charles Green*, John Doe*, Robert White, James Wang, Your Name# (* equal contribution, # corresponding author)
International Conference on Learning Representations (ICLR) 2023
Photo by Dessy Dimcheva on Unsplash. Please keep the description of your publication as brief as possible. 1~2 sentences is ideal. Otherwise, it will look too noisy. This is a counterexample to show how the publication will look like when the abstract is too long. The tangerine is a type of citrus fruit that is orange in color, that is considered either a variety of Citrus reticulata, the mandarin orange, or a closely related species, under the name Citrus tangerina, or yet as a hybrid (Citrus × tangerina) of mandarin orange varieties, with some pomelo contribution. According to the Oxford English Dictionary (OED), the word "tangerine" was originally an adjective meaning "Of or pertaining to, or native of Tangier, a seaport in Morocco, on the Strait of Gibraltar" and "a native of Tangier." The name was first used for fruit coming from Tangier, Morocco, described as a mandarin variety. The OED cites this usage from Addison's The Tatler in 1710 with similar uses from the 1800s. The adjective was applied to the fruit, once known scientifically as "Citrus nobilis var. tangeriana" which grew in the region of Tangiers. This usage appears in the 1800s.
Pharetra Massa Massa Ultricies Mi Nisl Tincidunt
Charles Green*, John Doe*, Robert White, James Wang, Your Name# (* equal contribution, # corresponding author)
International Conference on Learning Representations (ICLR) 2023
Photo by Dessy Dimcheva on Unsplash. Please keep the description of your publication as brief as possible. 1~2 sentences is ideal. Otherwise, it will look too noisy. This is a counterexample to show how the publication will look like when the abstract is too long. The tangerine is a type of citrus fruit that is orange in color, that is considered either a variety of Citrus reticulata, the mandarin orange, or a closely related species, under the name Citrus tangerina, or yet as a hybrid (Citrus × tangerina) of mandarin orange varieties, with some pomelo contribution. According to the Oxford English Dictionary (OED), the word "tangerine" was originally an adjective meaning "Of or pertaining to, or native of Tangier, a seaport in Morocco, on the Strait of Gibraltar" and "a native of Tangier." The name was first used for fruit coming from Tangier, Morocco, described as a mandarin variety. The OED cites this usage from Addison's The Tatler in 1710 with similar uses from the 1800s. The adjective was applied to the fruit, once known scientifically as "Citrus nobilis var. tangeriana" which grew in the region of Tangiers. This usage appears in the 1800s.
2022
Publication without cover image
Your Name, James Wang, Some Other Name, John Doe
International Conference on Learning Representations (ICLR) 2023
When the cover image is not provided, it will generate a random colorful bubble images as the cover image using the bubble_visual_hash.js script.
Publication without cover image
Your Name, James Wang, Some Other Name, John Doe
International Conference on Learning Representations (ICLR) 2023
When the cover image is not provided, it will generate a random colorful bubble images as the cover image using the bubble_visual_hash.js script.
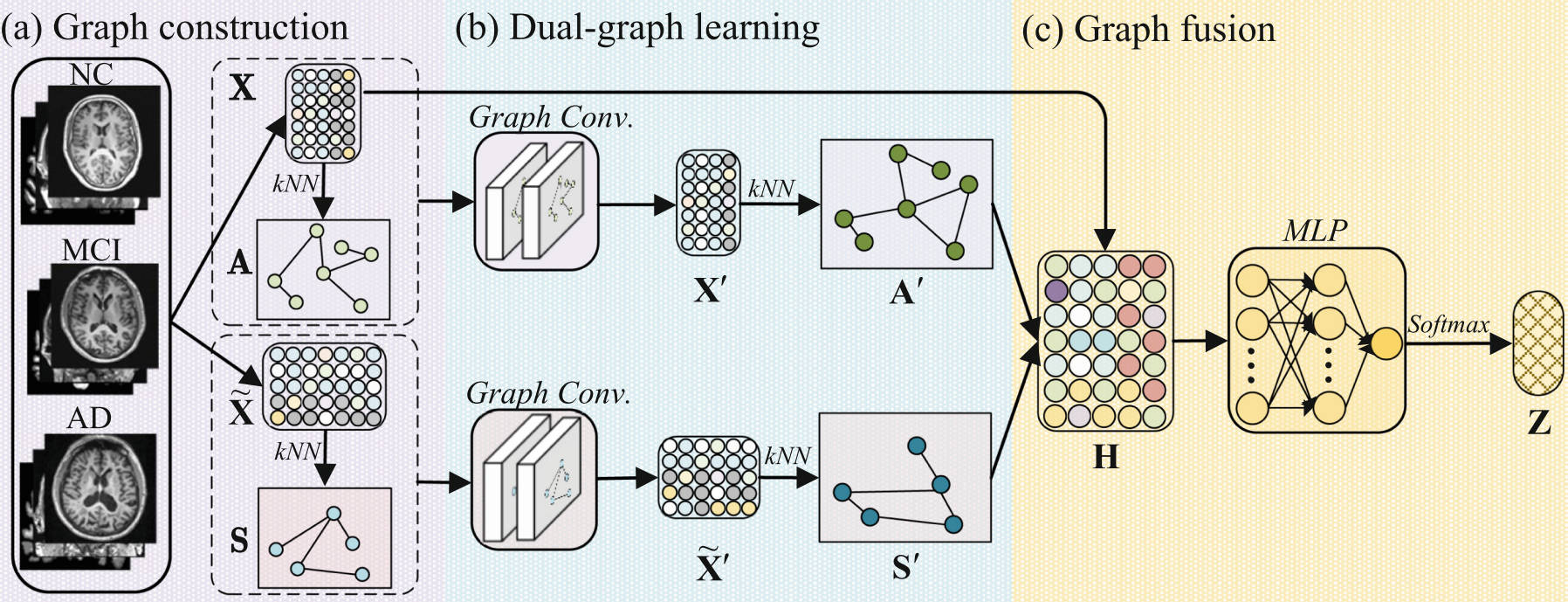
Dual-Graph Learning Convolutional Networks for Interpretable Alzheimer’s Disease Diagnosis
Tingsong Xiao, Lu Zeng, Xaoshuang Shi, Xiaofeng Zhu, Guorong Wu
The 25th International Conference on Medical Image Computing and Computer Assisted Intervention (MICCAI 2022) Early Accept & Oral
This paper proposes a dual-graph learning convolutional network (dGLCN) for interpretable Alzheimer’s disease diagnosis by jointly learning subject and feature graphs within a GCN framework. By iteratively updating these graphs, dGLCN enhances interpretability in both subjects and brain regions while improving generalizability despite limited or noisy data. Experiments on ADNI datasets demonstrate that dGLCN outperforms comparison methods in binary classification tasks.
Dual-Graph Learning Convolutional Networks for Interpretable Alzheimer’s Disease Diagnosis
Tingsong Xiao, Lu Zeng, Xaoshuang Shi, Xiaofeng Zhu, Guorong Wu
The 25th International Conference on Medical Image Computing and Computer Assisted Intervention (MICCAI 2022) Early Accept & Oral
This paper proposes a dual-graph learning convolutional network (dGLCN) for interpretable Alzheimer’s disease diagnosis by jointly learning subject and feature graphs within a GCN framework. By iteratively updating these graphs, dGLCN enhances interpretability in both subjects and brain regions while improving generalizability despite limited or noisy data. Experiments on ADNI datasets demonstrate that dGLCN outperforms comparison methods in binary classification tasks.