University of Florida.
University of Florida.Tingsong Xiao is a third-year PhD candidate in Computer Science at the University of Florida, supervised by Dr. Zhe Jiang. His research focuses on Deep Learning, Large Language Model (LLM), Generative Artificial Intelligence.
He earned his Bachelor of Engineering in Data Science and Big Data Technology from the University of Electronic Science and Technology of China (UESTC) in 2021, graduating with distinction. During his undergraduate studies, he conducted research on recommendation systems and medical image analysis. With a strong emphasis on medical applications, his current work focuses on developing innovative algorithms for AI in healthcare. He has published papers in prestigious conferences, including NeurIPS, AAAI, MICCAI, and ACM SIGSPATIAL. He has received recognitions such as the ACM SIGSPATIAL 2023 Best Paper Award and the MICCAI 2022 Student Travel Award. He is also an active contributor to the academic community, serving as a reviewer for leading journals and conferences such as NeurIPS, ICML, ICLR, and IEEE Transactions.
Warning
Problem: The current name of your GitHub Pages repository ("Solution: Please consider renaming the repository to "
http://".
However, if the current repository name is intended, you can ignore this message by removing "{% include widgets/debug_repo_name.html %}" in index.html.
Action required
Problem: The current root path of this site is "baseurl ("_config.yml.
Solution: Please set the
baseurl in _config.yml to "Education
-
 University of FloridaDepartment of Computer & Information Science & Engineering
University of FloridaDepartment of Computer & Information Science & Engineering
Ph.D. StudentSep. 2022 - present -
 University of Electronic Science and Technology of ChinaB.S. in Computer ScienceSep. 2017 - Jul. 2021
University of Electronic Science and Technology of ChinaB.S. in Computer ScienceSep. 2017 - Jul. 2021
Honors & Awards
-
2023, 2025
Program Committee
-
Association for the Advancement of Artificial Intelligence (AAAI)2024, 2025, 2026
-
Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems (NeurIPS)2023, 2024, 2025
-
International Conference on Learning Representations (ICLR)2022, 2023, 2024, 2025
-
International Conference on Machine Learning (ICML)2024, 2025
-
ACM SIGKDD Conference on Knowledge Discovery and Data Mining (KDD)2024, 2025
-
American Medical Informatics Association Annual Symposium (AMIA)2024, 2025
-
International Conference on Artificial Intelligence and Statistics (AISTATS)2025
-
International Conference on Acoustics, Speech, and Signal Processing (ICASSP)2025
-
International Joint Conference on Neural Networks (IJCNN)2025
-
European Conference on Artificial Intelligence (ECAI)2025
-
International Conference on Intelligent Systems for Molecular Biology (ISMB)2024
-
IEEE International Symposium on Biomedical Imaging (ISBI)2023
-
IEEE International Conference on Data Mining (ICDM)2023
-
International Conference on Medical Image Computing and Computer-Assisted Intervention (MICCAI)2022
Journal Reviewer
-
ACM Transactions on Intelligent Systems and Technology (TIST)
-
IEEE Transactions on Knowledge and Data Engineering (TKDE)
-
IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks and Learning Systems (TNNLS)
-
IEEE Transactions on Image Processing (TIP)
-
IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems for Video Technology (TCSVT)
-
IEEE Transactions on Computational Social Systems (TCSS)
-
IEEE Transactions on Multimedia (TMM)
-
Information Processing & Management (IP&M)
-
Communications of the ACM (CACM)
-
Journal of Medical Internet Research (JMIR)
-
Journal of the International Measurement Confederation
-
Future Generation Computer Systems
-
Information Sciences
-
Neural Networks
-
Neural Processing Letters
-
Pattern Recognition Letters
News
Selected Publications (view all )
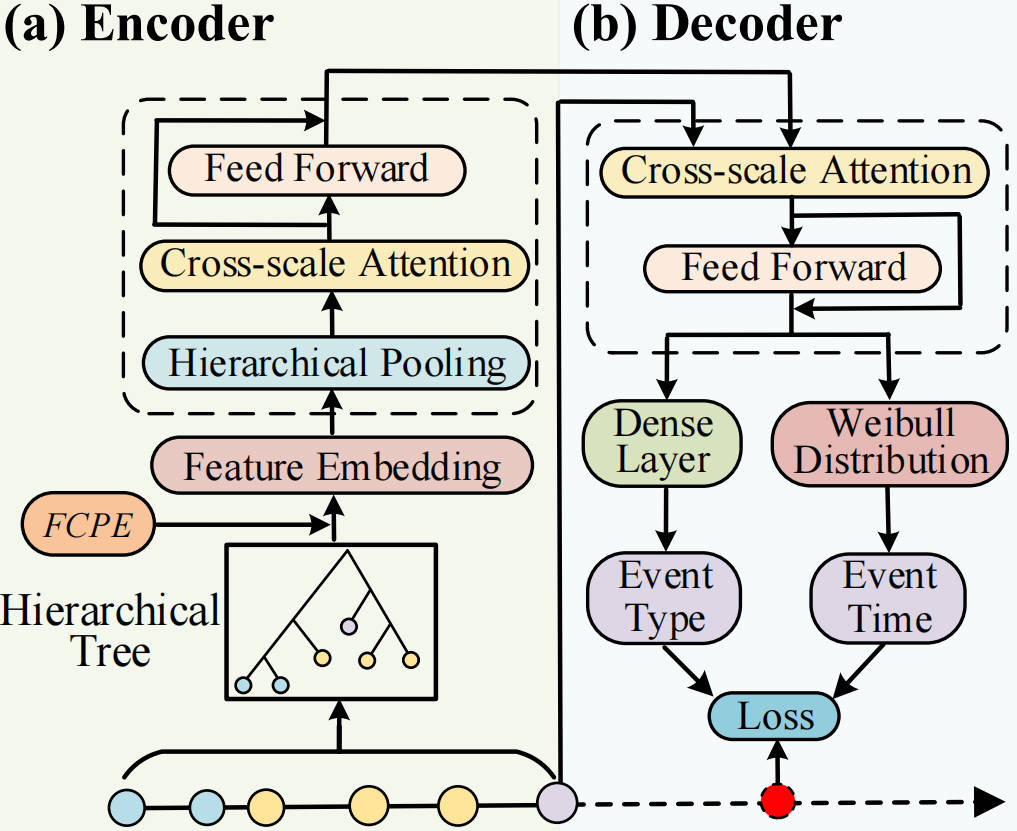
XTSFormer: Cross-Temporal-Scale Transformer for Irregular-Time Event Prediction in Clinical Applications
Tingsong Xiao, Zelin Xu, Wenchong He, Zhengkun Xiao, Yupu Zhang, Zibo Liu, Shigang Chen, My T. Thai, Jiang Bian, Parisa Rashidi, Zhe Jiang
The 39th Annual AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence (AAAI 2025)
Modeling irregularly timed clinical events from EHRs is challenging due to time irregularity, cyclical patterns, and multi-scale event interactions. We propose XTSFormer, a transformer-based model with cycle-aware time encoding and multi-scale attention to address these challenges.
XTSFormer: Cross-Temporal-Scale Transformer for Irregular-Time Event Prediction in Clinical Applications
Tingsong Xiao, Zelin Xu, Wenchong He, Zhengkun Xiao, Yupu Zhang, Zibo Liu, Shigang Chen, My T. Thai, Jiang Bian, Parisa Rashidi, Zhe Jiang
The 39th Annual AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence (AAAI 2025)
Modeling irregularly timed clinical events from EHRs is challenging due to time irregularity, cyclical patterns, and multi-scale event interactions. We propose XTSFormer, a transformer-based model with cycle-aware time encoding and multi-scale attention to address these challenges.
Spatial-Logic-Aware Weakly Supervised Learning for Flood Mapping on Earth Imagery
Zelin Xu, Tingsong Xiao, Wenchong He, Yu Wang, Zhe Jiang, Shigang Chen, Yiqun Xie, Xiaowei Jia, Da Yan, Yang Zhou
The 38th Annual AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence (AAAI 2024)
This work addresses the challenge of flood mapping on high-resolution Earth imagery with coarse, noisy labels by proposing a spatial-logic-aware weakly supervised learning framework. The framework integrates symbolic spatial logic inference with probabilistic learning and introduces a multi-resolution spatial reasoning algorithm to handle high-resolution imagery efficiently. Experiments on real-world flood datasets demonstrate superior prediction accuracy compared to traditional and neural-symbolic baselines.
Spatial-Logic-Aware Weakly Supervised Learning for Flood Mapping on Earth Imagery
Zelin Xu, Tingsong Xiao, Wenchong He, Yu Wang, Zhe Jiang, Shigang Chen, Yiqun Xie, Xiaowei Jia, Da Yan, Yang Zhou
The 38th Annual AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence (AAAI 2024)
This work addresses the challenge of flood mapping on high-resolution Earth imagery with coarse, noisy labels by proposing a spatial-logic-aware weakly supervised learning framework. The framework integrates symbolic spatial logic inference with probabilistic learning and introduces a multi-resolution spatial reasoning algorithm to handle high-resolution imagery efficiently. Experiments on real-world flood datasets demonstrate superior prediction accuracy compared to traditional and neural-symbolic baselines.
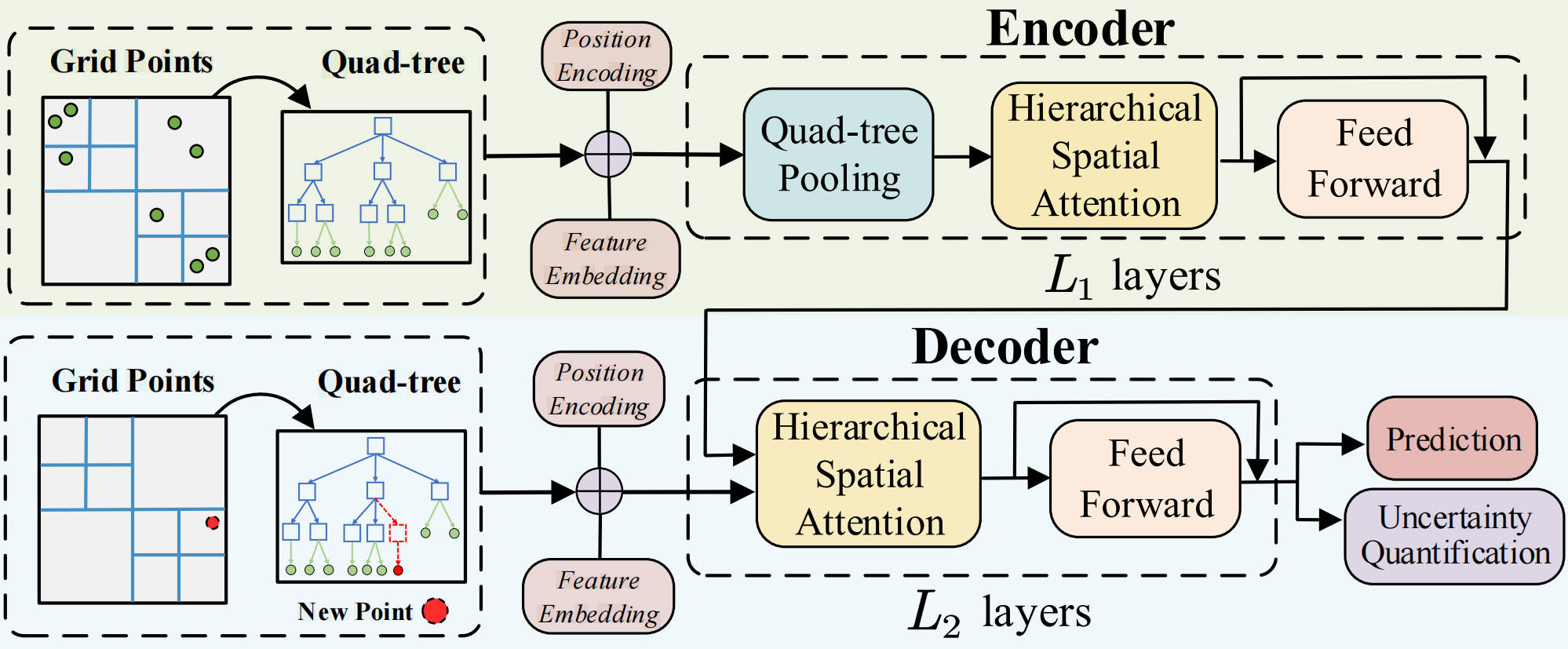
A Hierarchical Spatial Transformer for Massive Point Samples in Continuous Space
Wenchong He, Zhe Jiang, Tingsong Xiao, Zelin Xu, Shigang Chen, Ronald Fick, Miles Medina, Christine Angelini
The 37th Annual Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems (NeurIPS 2023)
This paper proposes a hierarchical spatial transformer for massive point samples, addressing challenges like long-range dependencies, irregular distributions, and high computational costs. Using quad-tree-based multi-resolution learning, efficient spatial attention, and uncertainty quantification, the model outperforms baselines and scales to one million points on a single NVIDIA A100 GPU.
A Hierarchical Spatial Transformer for Massive Point Samples in Continuous Space
Wenchong He, Zhe Jiang, Tingsong Xiao, Zelin Xu, Shigang Chen, Ronald Fick, Miles Medina, Christine Angelini
The 37th Annual Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems (NeurIPS 2023)
This paper proposes a hierarchical spatial transformer for massive point samples, addressing challenges like long-range dependencies, irregular distributions, and high computational costs. Using quad-tree-based multi-resolution learning, efficient spatial attention, and uncertainty quantification, the model outperforms baselines and scales to one million points on a single NVIDIA A100 GPU.
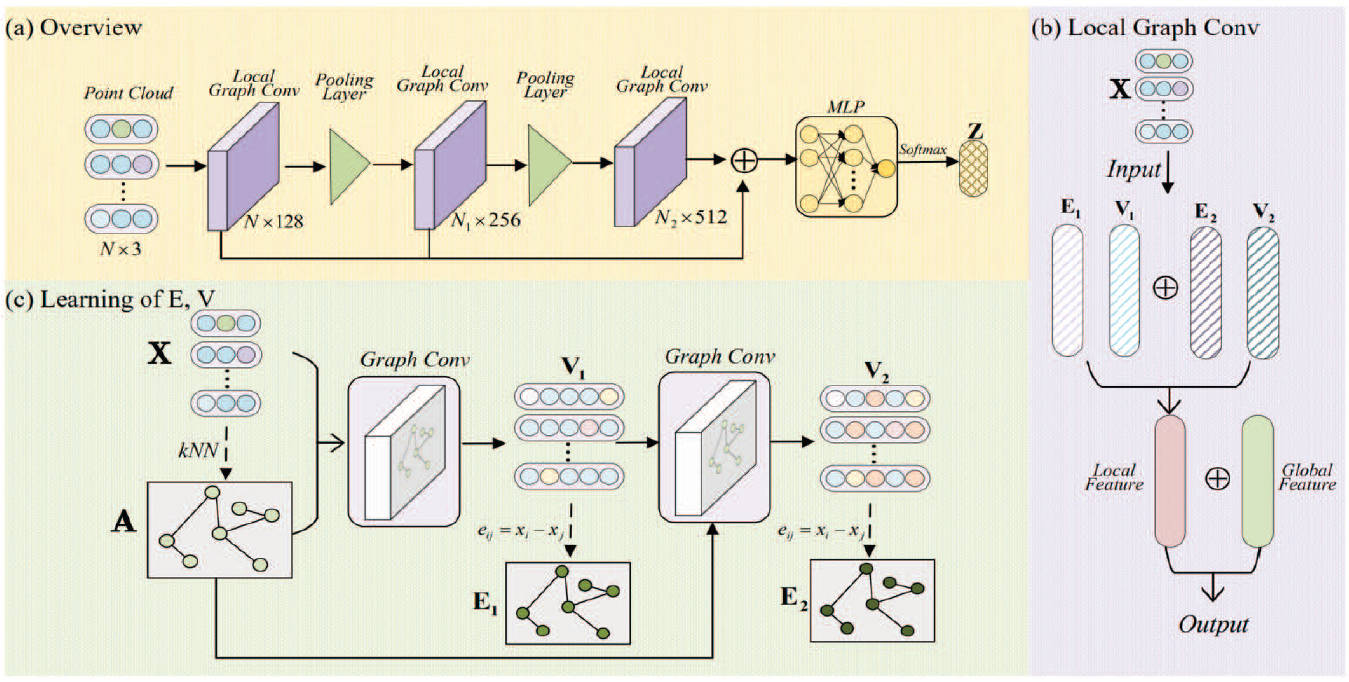
M-GCN: Multi-scale Graph Convolutional Network for 3D Point Cloud Classification
Jing Hu, Xincheng Wang, Ziheng Liao, Tingsong Xiao# (# corresponding author)
IEEE International Conference on Multimedia and Expo (ICME 2023)
This paper introduces a Multi-Scale Graph Convolutional Network (M-GCN) to enhance 3D point cloud analysis by leveraging multi-scale feature fusion for richer local topological representations. By extracting geometric features across scales, M-GCN improves the representation power of point clouds. Experiments on ModelNet40 demonstrate state-of-the-art performance in 3D point cloud classification.
M-GCN: Multi-scale Graph Convolutional Network for 3D Point Cloud Classification
Jing Hu, Xincheng Wang, Ziheng Liao, Tingsong Xiao# (# corresponding author)
IEEE International Conference on Multimedia and Expo (ICME 2023)
This paper introduces a Multi-Scale Graph Convolutional Network (M-GCN) to enhance 3D point cloud analysis by leveraging multi-scale feature fusion for richer local topological representations. By extracting geometric features across scales, M-GCN improves the representation power of point clouds. Experiments on ModelNet40 demonstrate state-of-the-art performance in 3D point cloud classification.
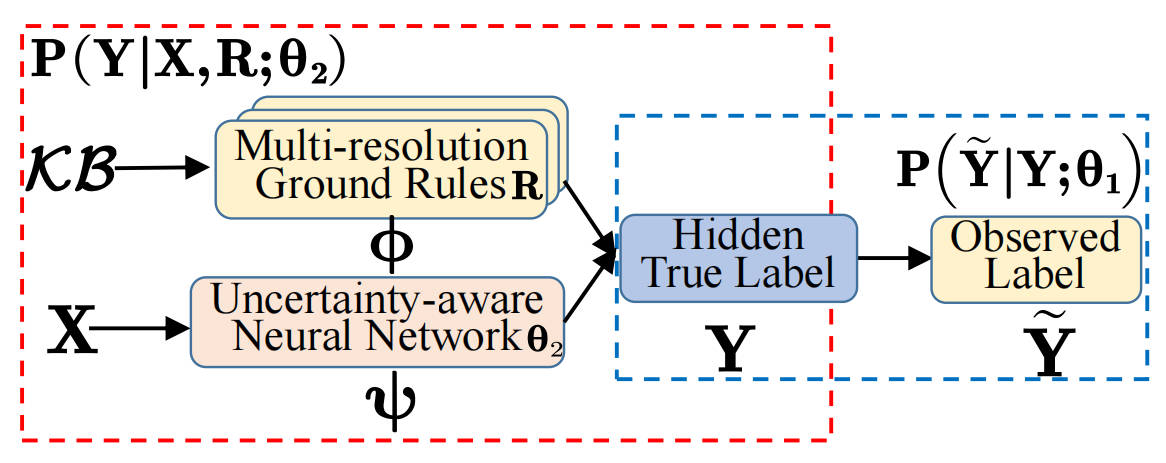
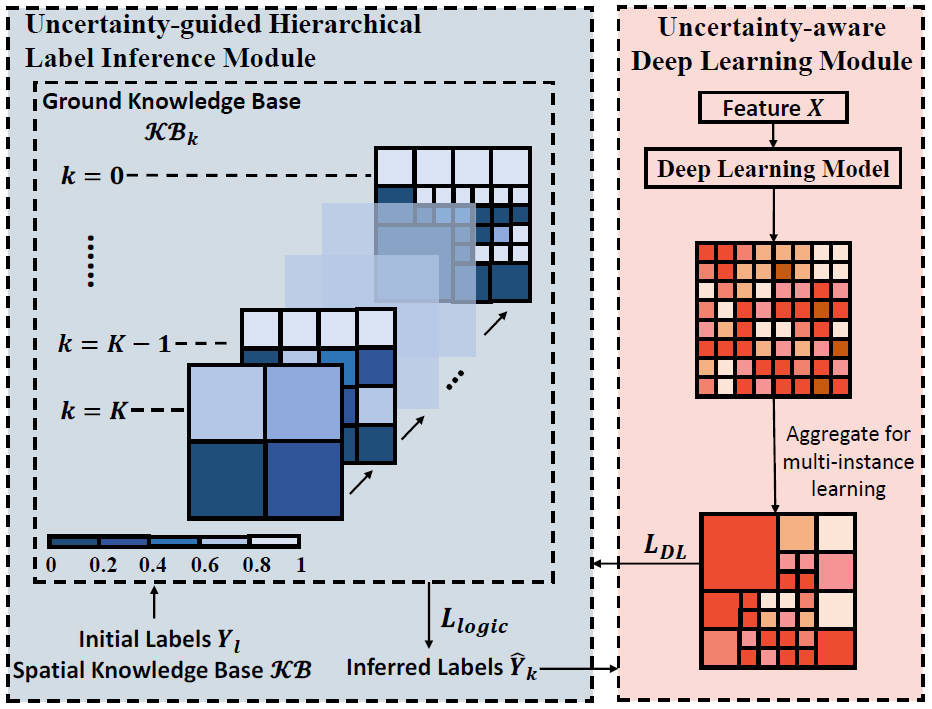
Spatial Knowledge-Infused Hierarchical Learning: An Application in Flood Mapping on Earth Imagery
Zelin Xu, Tingsong Xiao, Wenchong He, Yu Wang, Zhe Jiang
The 31st ACM International Conference on Advances in Geographic Information Systems (SIGSPATIAL 2023) Best Paper Award
This paper proposes a Spatial Knowledge-Infused Hierarchical Learning (SKI-HL) framework for Earth imagery with limited training labels, addressing challenges like sparse input labels, spatial uncertainty, and high computational costs. SKI-HL iteratively infers labels within a multi-resolution hierarchy using uncertainty-aware modules for selective label inference and neural network training. Experiments on flood mapping datasets demonstrate superior performance compared to baseline methods.
Spatial Knowledge-Infused Hierarchical Learning: An Application in Flood Mapping on Earth Imagery
Zelin Xu, Tingsong Xiao, Wenchong He, Yu Wang, Zhe Jiang
The 31st ACM International Conference on Advances in Geographic Information Systems (SIGSPATIAL 2023) Best Paper Award
This paper proposes a Spatial Knowledge-Infused Hierarchical Learning (SKI-HL) framework for Earth imagery with limited training labels, addressing challenges like sparse input labels, spatial uncertainty, and high computational costs. SKI-HL iteratively infers labels within a multi-resolution hierarchy using uncertainty-aware modules for selective label inference and neural network training. Experiments on flood mapping datasets demonstrate superior performance compared to baseline methods.
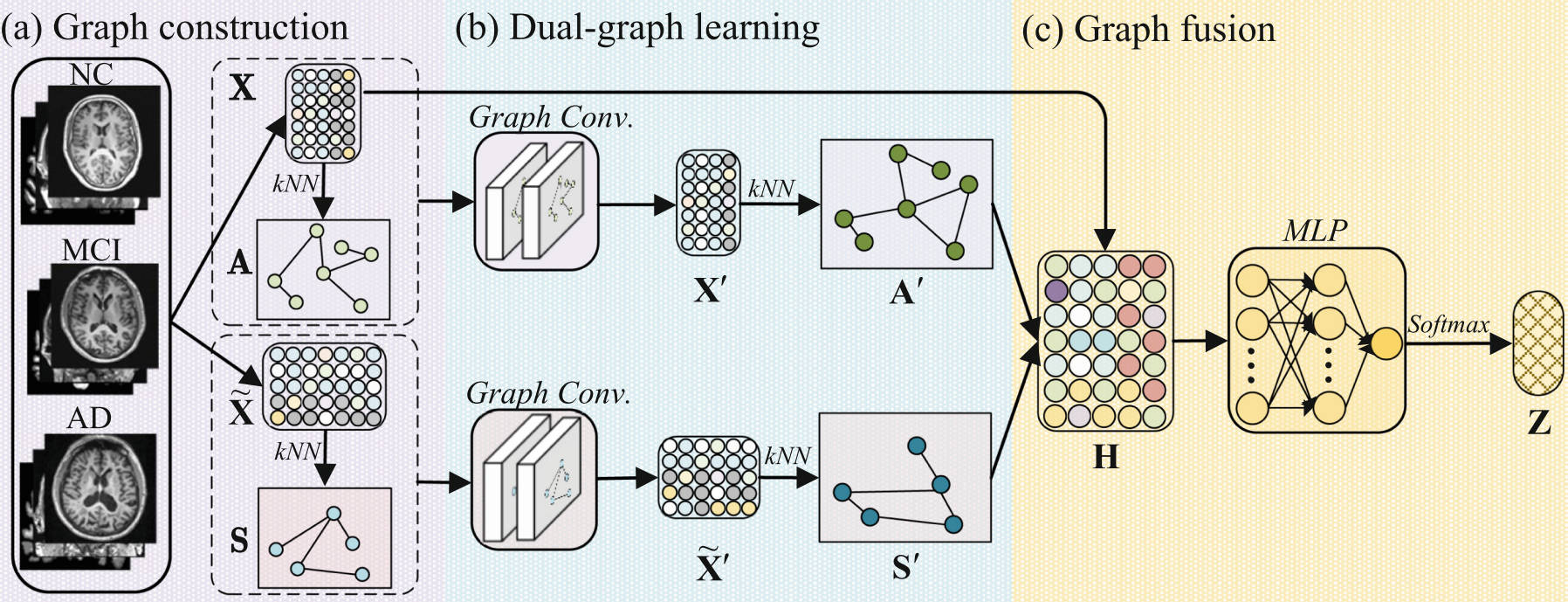
Dual-Graph Learning Convolutional Networks for Interpretable Alzheimer’s Disease Diagnosis
Tingsong Xiao, Lu Zeng, Xaoshuang Shi, Xiaofeng Zhu, Guorong Wu
The 25th International Conference on Medical Image Computing and Computer Assisted Intervention (MICCAI 2022) Early Accept & Oral
This paper proposes a dual-graph learning convolutional network (dGLCN) for interpretable Alzheimer’s disease diagnosis by jointly learning subject and feature graphs within a GCN framework. By iteratively updating these graphs, dGLCN enhances interpretability in both subjects and brain regions while improving generalizability despite limited or noisy data. Experiments on ADNI datasets demonstrate that dGLCN outperforms comparison methods in binary classification tasks.
Dual-Graph Learning Convolutional Networks for Interpretable Alzheimer’s Disease Diagnosis
Tingsong Xiao, Lu Zeng, Xaoshuang Shi, Xiaofeng Zhu, Guorong Wu
The 25th International Conference on Medical Image Computing and Computer Assisted Intervention (MICCAI 2022) Early Accept & Oral
This paper proposes a dual-graph learning convolutional network (dGLCN) for interpretable Alzheimer’s disease diagnosis by jointly learning subject and feature graphs within a GCN framework. By iteratively updating these graphs, dGLCN enhances interpretability in both subjects and brain regions while improving generalizability despite limited or noisy data. Experiments on ADNI datasets demonstrate that dGLCN outperforms comparison methods in binary classification tasks.